
The allure of residential properties lies in the emotional appeal of having a place to call home, whereas the commercial sector captivates with the promise of substantial financial gains. Given these distinctions, recognizing the importance of understanding the financial nuances and accounting strategies that underpin the management of these portfolios is essential for making informed investment choices. As you venture into the intricate world of real estate accounting, developing a keen awareness of the distinct financial landscapes characterizing both residential and commercial real estate becomes a top priority. Thus, by exploring the intricacies of ‘Residential vs. Commercial: Accounting for Your Real Estate Portfolio,’ you gain a comprehensive insight into the contrasting financial strategies and considerations that are vital for successfully navigating within these two divergent yet interconnected realms of the real estate market.
In the world of real estate, residential investments carry a deep connection to the emotional essence of homeownership, accompanied by the intricacies of rental income dynamics and the ever-shifting local housing market. Moreover, when it comes to accounting for residential portfolios, it’s essential to adeptly navigate the complexities of mortgage structures, various property valuation methodologies, and the nuances of property tax regulations. Conversely, delving into commercial real estate requires a sharp understanding of lease agreements, protocols for managing tenants, and the intricate world of commercial property valuation. Additionally, for effective management of commercial portfolios, one must master the dynamics of lease negotiations, as well as understand property maintenance costs and the impact of market trends on revenue streams. Consequently, comprehending the nuances and distinctions between residential and commercial real estate accounting becomes vital in the pursuit of maximizing returns and ensuring a balanced and diversified real estate investment portfolio.
I. Understanding the Distinctions Between Residential and Commercial Real Estate
In the dynamic realm of real estate, residential and commercial properties stand as two primary categories, each representing distinct segments within the market. Residential properties embrace a range of housing options, including single-family homes, condominiums, townhouses, and multifamily dwellings, serving as both primary residences and rental properties for individuals and families. On the flip side, commercial properties comprise diverse spaces such as retail outlets, office buildings, industrial facilities, and mixed-use developments, catering to businesses and enterprises for a multitude of commercial purposes.
There are a number of key distinctions between residential and commercial real estate, including:
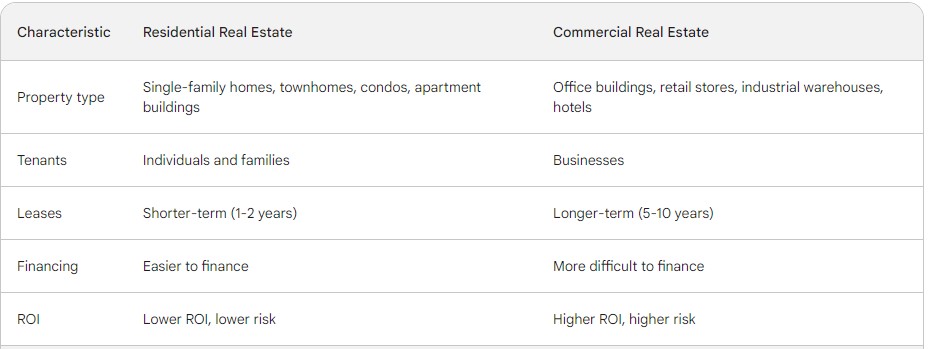
- Property type: Residential real estate is typically single-family homes or smaller multi-family units, while commercial real estate is typically larger and more specialized properties.
- Tenants: Residential real estate is typically leased to individuals and families, while commercial real estate is typically leased to businesses.
- Leases: Residential leases are typically shorter-term (1-2 years), while commercial leases are typically longer-term (5-10 years).
- Financing: Residential real estate is typically easier to finance than commercial real estate, as there are more government-backed financing options available.
- Return on investment (ROI): Commercial real estate has the potential to generate a higher ROI than residential real estate, but it also comes with a higher degree of risk.
Here is a table that summarizes the key distinctions between residential and commercial real estate:
When considering real estate investment options, it’s important to note that while residential properties generally offer stable rental income and long-term appreciation, commercial properties bring forth higher income potential, longer lease terms, and the opportunity for diversification across various asset classes. Therefore, recognizing these distinctions is crucial for investors, as it enables them to make informed decisions and adopt appropriate accounting practices that align with their investment objectives and risk tolerance.
II. Accounting Principles for Residential Real Estate Portfolios
When it comes to accounting for residential real estate portfolios, the application of specific principles and practices tailored to the unique characteristics of residential properties is imperative. Notably, key accounting considerations for residential real estate investors include the following:
- Rental Income and Expense Tracking: Implement a robust system for tracking rental income, including lease payments, security deposits, and ancillary rental fees, along with comprehensive expense management to accurately monitor property-related costs, such as maintenance, utilities, and property management fees.
- Tenant Management and Lease Agreements: Maintain meticulous records of lease agreements, tenant communications, and rental terms to ensure compliance with lease provisions, rental payment schedules, and property occupancy regulations, facilitating transparent and efficient tenant management within residential properties.
- Property Maintenance and Repair Reserves: Allocate sufficient reserves for ongoing property maintenance and repair expenditures, accounting for anticipated capital improvements, routine repairs, and unforeseen maintenance costs to preserve the value and attractiveness of residential properties for tenants and prospective buyers.
- Property Depreciation and Tax Benefits: Leverage depreciation schedules and tax benefits associated with residential properties to minimize tax liabilities and optimize after-tax returns, considering the allowable deductions for property depreciation, mortgage interest, and property taxes, as outlined in the U.S. tax code.
III. Accounting Strategies for Commercial Real Estate Portfolios

When it comes to commercial real estate portfolios, accounting demands a comprehensive understanding of industry-specific accounting strategies and best practices to maximize profitability and ensure regulatory compliance. Consequently, essential accounting considerations for commercial real estate investors include the following:
- Lease Management and Revenue Recognition: Implement robust lease management systems to monitor lease agreements, rent escalations, and tenant reimbursements, facilitating accurate revenue recognition and streamlined rental income reporting for various commercial properties, including retail, office, and industrial spaces.
- Property Valuation and Financial Reporting: Conduct regular property valuations and financial assessments to determine the fair market value of commercial properties, enabling investors to generate comprehensive financial reports, assess investment performance, and make informed decisions regarding property acquisition, disposition, or refinancing.
- Operational Expenditure Analysis: Analyze operational expenditures associated with commercial properties, including operating expenses, property taxes, insurance premiums, and common area maintenance (CAM) charges, to identify cost-saving opportunities, optimize cash flow management, and enhance the overall financial performance of commercial real estate assets.
- Capital Expenditure Planning and Budgeting: Develop structured capital expenditure plans and budgets for commercial properties to allocate funds for significant property improvements, renovations, and tenant improvements, fostering long-term asset appreciation, tenant satisfaction, and sustainable revenue growth within the commercial real estate portfolio.
IV. Comparative Analysis: Residential vs. Commercial Real Estate Accounting
A comparative analysis of residential and commercial real estate accounting provides investors with valuable insights into the distinct accounting methodologies, financial metrics, and performance indicators that define each asset class. By evaluating key performance indicators, such as net operating income (NOI), cash-on-cash return, and capitalization rate, investors can assess the relative merits and drawbacks of residential and commercial real estate investments, enabling them to make informed decisions based on their investment goals and risk tolerance.

Residential Real Estate Accounting:
- Emphasizes rental income stability and long-term capital appreciation.
- Focuses on tenant management, lease compliance, and routine property maintenance.
- Leverages tax benefits associated with property depreciation and mortgage interest deductions.
- Primarily targets individual investors, small-scale property management firms, and real estate investment trusts (REITs) focused on residential properties.
Commercial Real Estate Accounting:
- Emphasizes income diversification, long-term lease agreements, and property appreciation potential.
- Focuses on lease management, property valuation, and strategic capital expenditure planning.
- Leverages tax benefits associated with property depreciation and qualified leasehold improvements.
- Primarily targets institutional investors, real estate development firms, and commercial property management companies specializing in retail, office, and industrial properties.
V. Risk Management and Compliance in Real Estate Accounting
In the world of real estate investments, one can’t underestimate the importance of effective risk management and compliance measures. These measures play a vital role in ensuring the success and security of both residential and commercial portfolios, serving as shields against potential financial, legal, and operational risks that may arise. Therefore, prioritizing the implementation of risk mitigation strategies and compliance protocols tailored to the specific demands of residential and commercial properties is crucial for ensuring a secure and successful investment venture.
- Regulatory Compliance and Disclosure Obligations: Ensure adherence to local, state, and federal regulations governing residential and commercial real estate transactions, lease agreements, and property management practices, fostering transparency, accountability, and legal compliance within the real estate portfolio.
- Insurance Coverage and Liability Protection: Secure comprehensive insurance coverage, including property insurance, liability insurance, and landlord insurance, to mitigate the financial impact of unforeseen events, property damages, tenant disputes, and legal liabilities associated with residential and commercial real estate holdings.
- Market Risk Assessment and Portfolio Diversification: Conduct regular market risk assessments and portfolio diversification analyses to identify potential market fluctuations, occupancy risks, and industry-specific challenges, enabling investors to implement proactive risk management strategies and optimize the overall risk-adjusted return on investment within the real estate portfolio.
- Internal Controls and Corporate Governance: Establish robust internal controls and corporate governance frameworks to monitor financial transactions, prevent fraudulent activities, and ensure ethical business practices, fostering a culture of transparency, integrity, and responsible stewardship within the residential and commercial real estate investment ecosystem.
VI. Emerging Trends in Residential and Commercial Real Estate Accounting
In the ever-evolving world of real estate accounting, the landscape is continually shaped by emerging trends and technological advancements. These developments redefine accounting practices, financial reporting standards, and operational efficiencies within the real estate industry. It’s important to note that some of the prominent trends influencing residential and commercial real estate accounting include:
- Technology Integration and Digital Transformation: The integration of advanced technologies, including cloud-based accounting software, data analytics tools, and artificial intelligence (AI) applications, is revolutionizing financial reporting, lease management, and portfolio analysis within residential and commercial real estate accounting practices.
- Sustainability and Environmental Reporting: The growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental stewardship is driving the adoption of sustainability accounting frameworks and environmental reporting standards, encouraging investors to incorporate eco-friendly initiatives, energy-efficient systems, and green building certifications within their residential and commercial real estate portfolios.
- Regulatory Compliance and Lease Accounting Standards: The evolving regulatory landscape and lease accounting standards, such as the Financial Accounting Standards Board’s (FASB) Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) 842 for lease accounting, are reshaping residential and commercial real estate accounting practices, necessitating comprehensive compliance measures and enhanced financial disclosures for lease agreements and property transactions.
- Data Security and Privacy Measures: Heightened awareness of data security and privacy concerns is prompting investors to prioritize data encryption, secure communication protocols, and robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive financial information, tenant records, and confidential business data within residential and commercial real estate accounting systems.
VII. Best Practices for Optimizing Residential and Commercial Real Estate Accounting
To optimize residential and commercial real estate accounting practices and maximize the financial performance of real estate portfolios, investors should consider implementing the following best practices:
- Integrated Accounting Software Solutions: Utilize integrated accounting software solutions tailored to the specific requirements of residential and commercial real estate accounting, enabling streamlined financial reporting, automated lease management, and comprehensive portfolio analysis for informed decision-making.
- Continuous Professional Development and Training: Invest in continuous professional development and training programs for accounting professionals, property managers, and real estate investment advisors, fostering a culture of expertise, innovation, and strategic leadership within the residential and commercial real estate investment landscape.
- Ethical Standards and Corporate Governance: Promote ethical standards and corporate governance principles that prioritize transparency, integrity, and accountability in financial reporting, property management, and stakeholder communications, establishing a strong reputation for responsible real estate investment practices and investor relations.
- Proactive Risk Management and Compliance Measures: Develop proactive risk management strategies and compliance measures that encompass comprehensive risk assessments, regulatory compliance reviews, and internal control audits, fostering a proactive approach to identifying and mitigating risks within residential and commercial real estate portfolios.
- Collaborative Stakeholder Engagement: Foster collaborative stakeholder engagement and transparent communication with tenants, property owners, regulatory authorities, and industry associations, fostering a culture of trust, partnership, and shared accountability within the residential and commercial real estate investment ecosystem.
VIII. Case Studies: Real-world Applications of Residential and Commercial Real Estate Accounting
When delving into the realm of real estate accounting, real-world case studies serve as valuable guides, offering practical insights into the application of residential and commercial real estate accounting principles, strategies, and best practices. These case studies shed light on successful approaches to optimizing financial performance and achieving sustainable growth within diverse real estate portfolios. Here are two case studies illustrating the effective implementation of residential and commercial real estate accounting practices:

Residential Real Estate Case Study:
The Peterson Family Residential Portfolio
Let’s take a look at the Peterson family, a group of individual investors who have made a mark in the real estate world. Over the years, they’ve built a diverse portfolio of single-family homes and multifamily properties across various bustling metropolitan areas. Through the smart use of integrated accounting software solutions, proactive tenant management strategies, and a strong focus on sustainable property maintenance practices, the Peterson family has achieved remarkable success. They’ve not only ensured a steady stream of rental income but have also kept vacancy rates to a minimum, all the while preserving the long-term value of their residential real estate portfolio.
Commercial Real Estate Case Study:
Downtown Office Tower Development Project
Now, let’s turn our attention to a prominent real estate development firm that has left an indelible mark on the industry. Recently, they undertook a groundbreaking downtown office tower development project, employing cutting-edge lease management software, conducting thorough financial feasibility studies, and embracing sustainable building design principles. These strategic moves allowed them to attract high-profile corporate tenants and achieve optimal lease rates. As a result, their commercial real estate development venture not only secured a robust return on investment but also garnered significant industry recognition, solidifying their position as industry leaders.
IX. Conclusion: Optimizing Your Real Estate Portfolio Accounting Strategy
When faced with the decision to invest in residential or commercial real estate, one must embark on a journey of understanding. It’s crucial to grasp the distinctive accounting practices, financial considerations, and risk management strategies associated with each asset class. By embracing best practices, leveraging integrated accounting software solutions, and giving priority to proactive risk management measures, investors can chart a path toward optimizing the financial performance of their residential and commercial real estate portfolios. Through these efforts, they not only achieve sustainable growth but also cultivate a strong competitive edge within the dynamic and ever-evolving landscape of real estate investment.

Contact Us

To learn more about how our expert accounting services can support your residential and commercial real estate portfolio accounting needs and optimize your investment performance, reach out to us today:
📞 Phone: 217-788-0750
📧 contact@taxstra.com
Our dedicated team of real estate accounting professionals is committed to providing tailored solutions and strategic guidance to help you maximize the financial potential of your real estate portfolio and achieve long-term success in the dynamic and competitive real estate market. Get in touch with us to embark on a journey toward optimizing your residential and commercial real estate accounting strategy today.
